AdTech has become increasingly advanced, offering advertisers the ability to reach their target audiences with unprecedented precision. However, this practice often involves the collection and utilization of personal information without users’ knowledge or consent, leading to serious privacy concerns.
As a result, governments worldwide are taking steps to protect users’ personal information online, recognizing the need to balance the benefits of ad targeting with the right to privacy. This has led to a shift in how AdTech works as companies seek to adapt to this new privacy-focused world.
The emergence of privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) has been a key development in this space. PETs are designed to help companies protect user privacy while still enabling them to collect and use data for programmatic advertising.
In this blog post, we will explore the various types of PETs available and provide examples of how they are being used in AdTech today.
Key Points
- Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) are tools and techniques used to protect user privacy and minimize the amount of data processed by companies.
- They are adopted in industries that process large amounts of personal and sensitive data.
- PETs focus on minimizing the use of personal data, maximizing data security, and minimizing the amount of data processed.
- Examples of PETs include encryption, anonymization, virtual private networks, privacy-preserving APIs, trusted execution environments, on-device learning, privacy-preserving data mining, differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and multi-party computation.
- The use of PETs has enabled the creation of many projects in the AdTech industry, including universal IDs, Google Privacy Sandbox, SKAdNetwork, PCM and PAIR.
Context
Going back a decade or so, companies in the programmatic advertising industry operated with very little regard for user privacy. Companies would collect large amounts of user data and use it to power everything from ad targeting to measurement.
But over the past few years, governments and tech companies have started to directly address the user privacy concerns by introducing new laws and making changes to how user data can be collected.
Law regulators across the world are working to improve the privacy of Internet users by introducing laws designed to regulate the collection, storage, and processing of personal data. Governments have enacted bills such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Digital Markets Act (DMA), and Digital Services Act (DSA) in the European Union, Lei Geral de Proteçao de Dados in Brazil, and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States to establish standards for data protection. These laws are designed to ensure that individuals have control over their personal information and that businesses handle it responsibly, transparently, and securely.
Tech companies have been working on increasing user privacy by changing their software and devices. For example, Apple Safari and Mozilla Firefox have recently added new privacy features. It is expected that Google Chrome will do the same in 2024. These web browsers are moving away from the use of third-party cookies and user IDs, which are used to track individual users across websites, and instead favor anonymized browsing.
This approach prevents online advertisers from identifying users on an individual basis, thereby putting an end to the practice of 1-1 ad targeting, which involves delivering personalized ads to users based on their browsing behavior.
The last piece of this puzzle is how the AdTech ecosystem responds to these changes. Publishers, advertisers, and AdTech companies are adapting privacy-enhancing technologies to preserve users’ privacy while delivering personalized advertising.
We Can Help You Build an AdTech Platform
Our AdTech development teams can work with you to design, build, and maintain a custom-built AdTech platform for any programmatic advertising channel.
What Are Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)?
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) is an umbrella term for tools, technologies, and techniques used to protect users from cyberattacks, maintain their privacy, and minimize the amount of data processed by companies.
Privacy-enhancing technologies are commonly used in industries that process large amounts of personal and sensitive data, such as banking, insurance, health, government, marketing, and advertising.
PETs help ensure data is secure by focusing on three key pillars:
- Minimizing the collection and use of personal data.
- Maximizing data security to protect consumer privacy.
- Minimizing the amount of data processed.
Some examples of privacy-enhancing technologies include:
- Minimization techniques
- Encryption
- Anonymization/pseudonymization
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
- Privacy-preserving APIs
- Trusted execution environment (TEE)
- On-device learning/federated learning (FL)
- Privacy-preserving data mining (PPDM)
- Differential privacy (DP)
- Homomorphic encryption (HE)
- Multi-party computation (MPC)
There are other technologies dedicated to and utilized in the AdTech industry, which we will expand on in the next section
Examples of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
In order to deliver targeted and relevant ads, AdTech platforms process vast amounts of data, including personally identifiable information (PII) and personal data.
Privacy-enhancing technologies can play a key role in ensuring this data is kept secure and protecting a user’s privacy across all layers in the programmatic advertising and AdTech ecosystem.
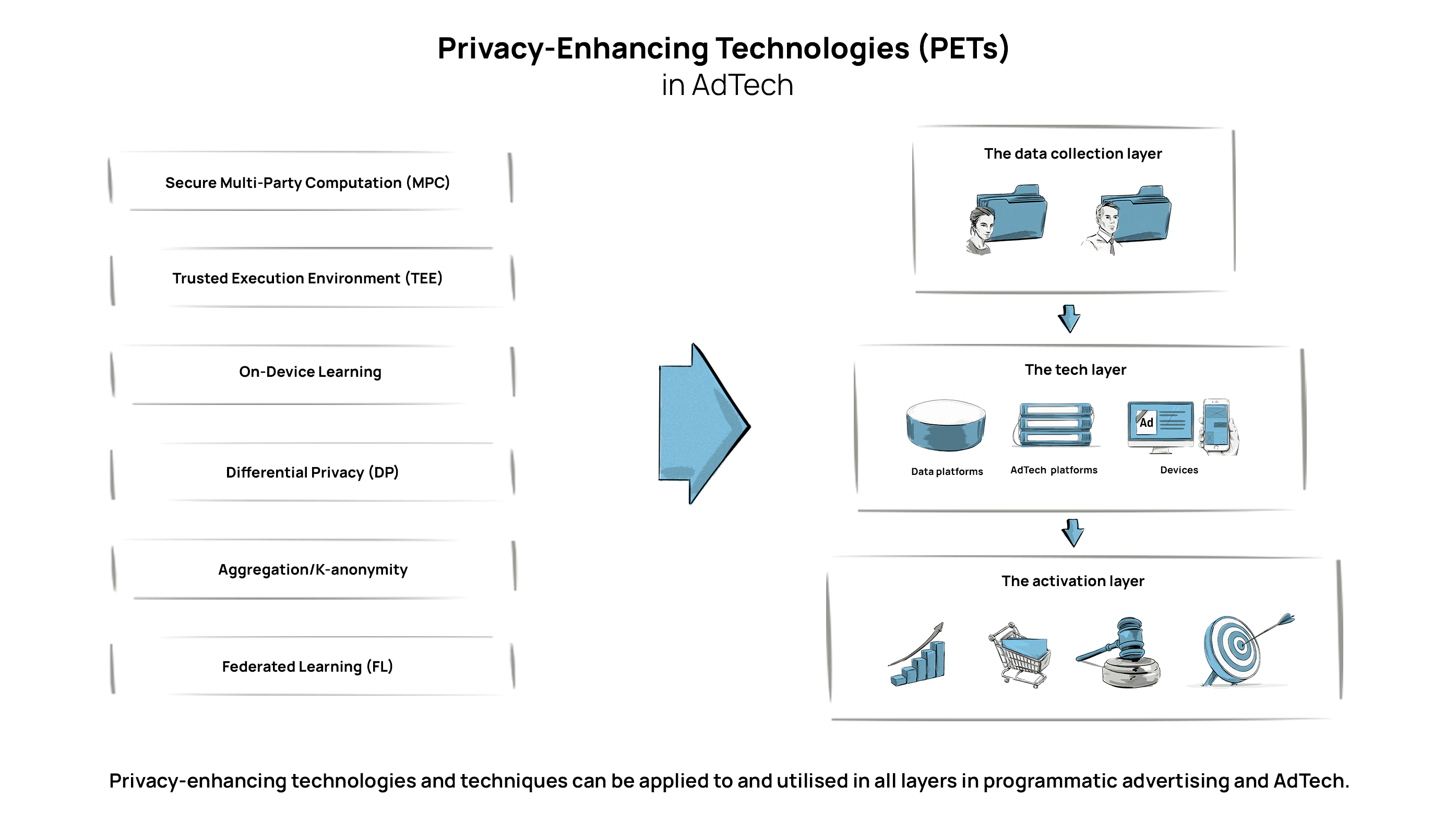
Most AdTech solutions that incorporate PETs combine one or more of the following techniques:
Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC)
Secure multi-party computation (MPC) is a technique that enables two or more entities to share encrypted data through multiple nodes/servers and gain insights without learning about each other’s data. Private Set Intersection (PSI), a cryptographic protocol that allows two parties to compute the intersection of their sets while keeping the contents of their sets private, is an MPC technique.
Trusted Execution Environment (TEE)
While they share some similarities with MPCs, Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) differ by enabling operations within a single server. TEEs use secure hardware with cryptographic protections to process data in a confidential computing environment, ensuring security and data privacy during data processing.
On-Device Learning
This technique is an algorithm trained on historical data, such as consumer interests or conversions, and is used to make predictions. The information is processed directly on the device, with no user information being sent back to the server.
Differential Privacy (DP)
Differential privacy is a technique used to analyze a dataset that provides a formal privacy guarantee by controlling the amount of privacy loss through mathematical methods. As DP is an algorithmic property, it can be applied uniformly to different data sets, thus protecting an individual’s identity from reconstruction or re-identification. DP can also be combined with other privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) as part of a comprehensive approach.
Aggregation/K-anonymity
This technique involves aggregating data to a minimum privacy threshold, ensuring that the result includes at least a minimum number of data points with identifiers removed, commonly referred to as “k.”
Federated Learning (FL)
Federated Learning is a machine-learning technique that enables models to be trained on decentralized data across multiple parties without exchanging any information.
The Purpose of Using Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in AdTech
As technology continues to advance so does the need for privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) in the AdTech industry. The basic purpose of using PETs in AdTech is to protect users’ personal information and prevent it from being used for unauthorized purposes.
However, AdTech not only processes data but also collects it, shares it between parties, and computes and utilizes it to power various programmatic advertising processes.
PETs can be used to increase security and user privacy for the following processes:
Data Collection
PETs can help organizations comply with data privacy regulations and avoid the potential legal and financial consequences of non-compliance when collecting data. Privacy-enhancing technologies also enable data minimization, which reduces the risk of data breaches, ensures that personal data is only collected for a specific and legitimate purpose, and decreases the space needed to keep data.
Identification
Without privacy-enhancing technologies, personally identifiable information and even sensitive data could be leaked. AdTech companies can protect this information from cyber attacks and data breaches by encrypting the data. There are many different techniques for encrypting data, but the three main ones are symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, and hashing.
Data Sharing Between Parties
Running advertising campaigns demands collaboration, such as data sharing between different AdTech platforms. However, this can also increase privacy concerns if not handled transparently and responsibly.
To keep the data safe and secure, AdTech companies can use encryption, secure multi-party computation, and differential privacy to exchange data confidentiality. Also, by using PETs, they can state who can have access to the data, which will minimize the risk of unauthorized access to it.
Data Processing
A set of procedures, such as computation, analysis, and measurement, are run on data every time an ad is served to a user.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) play a crucial role in ensuring that personal data remains secure and confidential during these procedures. For example, PETs like differential privacy enable the analysis of anonymized user data without revealing personal information, such as personal identifiers or browsing history.
Ad Targeting
Advertisers want to show relevant ads to their audiences and provide personalized experiences to their users. PETs, such as federated learning, allow them to display ads by processing data on a user’s device, rather than sending it to an external server. This approach reduces the possibility of personal data being shared with multiple companies.
Use Cases of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in AdTech
While you may not have heard about PETs, you’ve probably come across AdTech platforms and processes that incorporate these technologies.
Below are some of the main examples of privacy-enhancing technologies in AdTech.
Universal IDs
PETs can be used to generate a universal ID in a privacy-preserving way. For example, companies can apply a hashing algorithm, such as SHA-256, to an email address or phone number to produce an ID. So instead of using a user’s actual email address as the universal ID, companies can use the hashing algorithm to produce a random string of numbers and letters and use that as the ID.
This not only prevents a user’s raw data (i.e., the email address) from being used, but it also protects their privacy, as the hashed ID can’t be unscrambled once it’s been hashed. This ensures that the universal ID cannot be traced back to an individual.
Google’s Privacy Sandbox
Privacy Sandbox aims to replace the processes carried out by third-party cookies by utilizing advanced privacy techniques such as differential privacy, k-anonymity, and on-device processing.
Additionally, it helps to minimize other forms of tracking, like fingerprinting, by limiting the amount of information websites can access, ensuring that your personal information remains confidential, protected, and secure.
Data Clean Rooms
There are many different use cases of data clean rooms in the context of advertising. In an interview with Michael Sweeney, Head of Marketing at Clearcode, Gowthaman Ragothaman from Aqilliz shared some concepts on how brands can utilize data clean rooms for ad targeting, audience targeting, and measurement.
Encryption and double blinding for data inputs, differential privacy in running queries, injecting data noise, maintaining k-anonymity thresholds, are some of the techniques used in DCRs.
SKAdNetwork
SKAdNetwork is a privacy-centric API operated by Apple. For marketers running ad campaigns on iOS-powered devices, this system provides insights into campaign attribution that are anonymous, aggregated, and delayed.
Private Click Measurement
Private Click Measurement (PCM) by Apple was created for measuring ad clicks across websites and from iOS apps to websites. PCM uses on-device processing, differential privacy, blinded signatures and data minimization to ensure that user data is protected.
Publisher Advertiser Identity Reconciliation
Google’s Publisher Advertiser Identity Reconciliation (PAIR) enables publishers and advertisers to privately and securely reconcile their first-party data for audiences who have visited both a publisher’s and an advertiser’s website.
The solution works by allowing advertisers and publishers to activate encrypted first-party data that is specific to their sites via aggregation. This ensures that no data related to individual users is shared between parties, and the aggregated data is only readable and relevant in the context of their direct relationship.
MPC In an SSP
Magnite, a leading AdTech company, utilizes a form of technology called MPC to support activation without accessing raw data. Advertisers and publishers encrypt their data, such as first-party publisher lists or advertiser customer lists, using MPC.
The encrypted data is then sent to Magnite, who can match and create synthetic stable IDs using the data. These IDs can then be used to activate the data without accessing the raw data itself.
Private Computation
Meta uses multi-party computation to improve its ad targeting capabilities while preserving user privacy. The system allows Meta to analyze encrypted user data to identify trends and patterns without accessing the raw data itself. This enables Meta to provide more personalized ads without compromising user privacy.
The Future of Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in AdTech
To define the future of PETs, we need to take into consideration multiple factors, such as the growing awareness about privacy protection on the Internet, technological changes, new legal regulations, and the ongoing debate about privacy among publishers, advertisers, and organizations representing their interests.
Consumers and governments recognize the importance of privacy in the digital age. This consciousness will drive the wide adoption of PETs and the creation of new regulations around the topic, similar to how the GDPR, LGPD, CCPA, and the IAB Tech Lab’s TCF have been adopted. These, and other, legal frameworks will require companies to incorporate PETs into their AdTech technologies and processes to ensure they are compliant with various privacy laws.
Some advertisers and publishers have already recognized the benefits of PETs, such as an increase in consumer trust and reduced risk of data breaches.
As a result, more and more companies will dedicate budgets to new solutions such as data clean rooms to leverage PETs in their AdTech efforts.
Moreover, various technologies will go through different stages of development. The current priority lies in providing more granular control over the use of personal data, so in the nearest future, we can expect to see advancements and more sophistication in this field.
The last important aspect of the development of PETs is working on providing standardization.
The IAB Tech Lab has established a dedicated group to develop standards for PETs in AdTech. This group is made up of representatives from advertisers, publishers, technology providers, and privacy advocates.
Their goal is to develop a set of standardized protocols for PETs that can be adopted by the industry. This standardization will help to ensure that PETs are effective and consistent across the industry.
To summarize, PETs will definitely play an increasingly important role in AdTech in the coming years.
Do you want to learn why companies should start PETs into their businesses? Read Clearcode’s piece in Exchange Wire’s Industry Review 2023.
We Can Help You Build an AdTech Platform
Our AdTech development teams can work with you to design, build, and maintain a custom-built AdTech platform for any programmatic advertising channel.