“Where is Everybody?” This somewhat famous question was asked by Enrico Fermi, a physicist known for the Fermi paradox, when pondering why no alien lifeform has ever contacted planet Earth, given that there are about 100 Earth-like planets in the universe for every grain of sand in the world.
If you are unfamiliar with the Fermi paradox, here’s a short explanation:
The Fermi paradox is a conflict between arguments of scale and probability that seem to favor intelligent life being common in the universe, and a total lack of evidence of intelligent life having ever arisen anywhere other than on the Earth.
While scientists may not have the means to go out and find human-like life in the far corners of the universe, there’s nothing stopping marketers and advertisers from finding people who look and behave like their existing customers in the far corners of the Internet, via a process known as look-alike modeling.
What is Look-alike Modeling?
Look-alike modeling is essentially finding groups of people (audiences) who look and act like your best, most profitable customers. For example, let’s say you run an ecommerce store and you’ve identified that your best audience are people whose average purchase is over $100, buy cosmetics and perfumes, and make a purchase at least twice a month; look-alike modeling would allow you to find more people like that.
How Does Look-alike Modeling Work?
Like with most things in online advertising and marketing, look-alike modeling works by utilizing data and algorithms. For that reason, look-alike modeling is often conducted in a data-management platform (DMP), as it provides advertisers and marketers with means, tools, and resources needed to carry out look-alike modeling. Some demand-side platforms (DSPs) also provide functionality that allows you to create look-alike models.
The first step in conducting look-alike modeling involves collecting data, lots of data.
In order for look-alike models to produce accurate results, different types of data (i.e. first-, second-, and third-party data) needs to be collected from a range of online and offline sources.
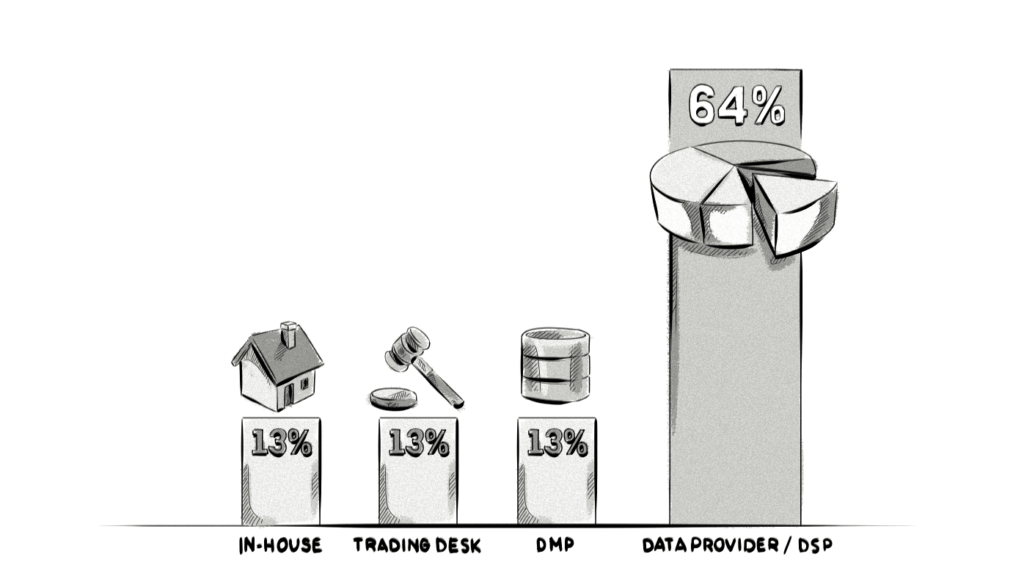
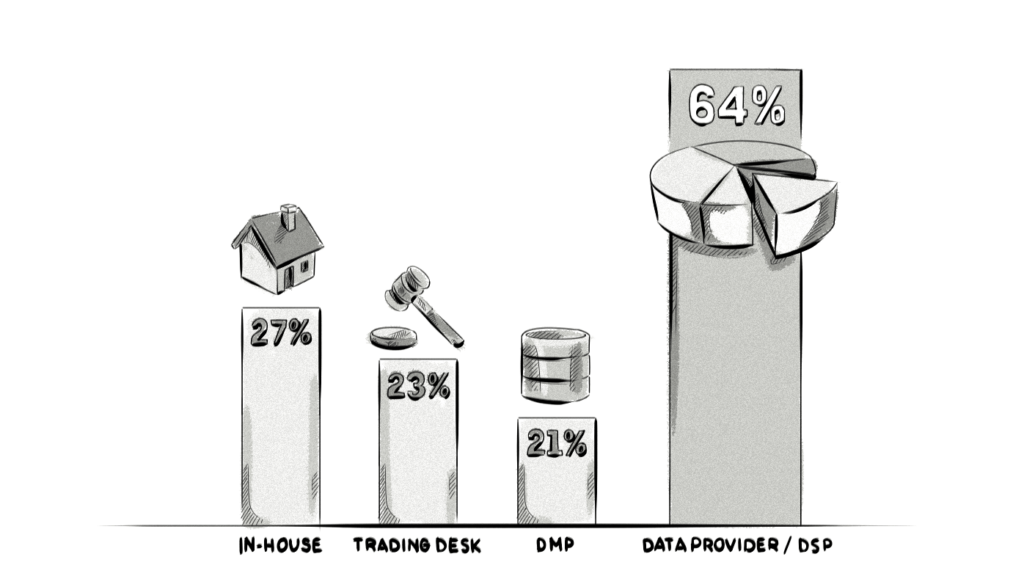
Each business will source their data from different places. For example, a survey conducted by eXelate in conjunction with Digiday shows that advertisers and ad agencies prefer to obtain their data from data providers/DSPs. Online marketers on the other hand would obtain their data from other sources, such as CRM systems, third-party data providers, web-analytics tools, marketing-automation platforms, etc.
Data sources used by advertisers and ad agencies to conduct look-alike modelling:
The second step is to define the attributes and behaviors of your most valuable customers, like the ones mentioned above.
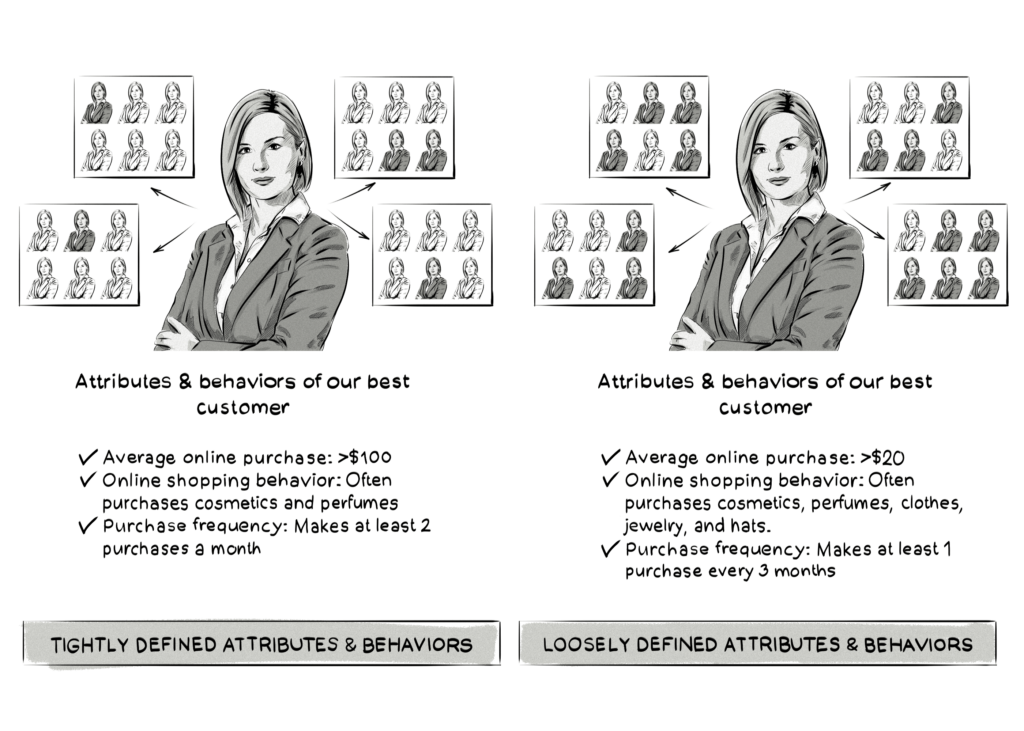
The stricter your look-alike model is (the more attributes you define), the better chance you have of finding your target — albeit smaller — audience, which will allow you to improve campaign performance. However, you could be less strict with the look-alike model (i.e. define less attributes and behaviors) if your goal is to focus on overall reach and awareness rather than higher conversion rates.
Using the ecommerce store example mentioned earlier, the image below shows the difference between a look-alike model that has tightly defined (more) attributes and behaviors, and one that has loosely defined (less) attributes and behaviors.
The third step involves using algorithms to extend the audience based on the look-alike model.
The DMP or DSP would analyze the seed audience (the pre-defined best customers) and then apply proprietary algorithms to the data you’ve collected in order to find user profiles that match the seed audience.
It’s kind of like a game of concentration, except you only turn over one main card and then collect all the other cards that match it.
What Can Look-alike Modeling Be Used For?
Prospecting and Increasing Campaign Reach
As you’ve probably already worked out, look-alike modeling is mainly used for prospecting, which involves finding new potential customers and/or visitors. However, it can also be used to extend the reach of online advertising campaigns.
Let’s say you target audiences based on a set of attributes (e.g. age, gender, location, etc.). By applying look-alike modeling to your campaigns, you can find similar customers who perhaps don’t fit your current audiences either because we don’t have enough data (e.g. we lack the attributes needed to make a match) or they don’t fit your current audiences (i.e. they consists of other attributes) but are still similar in many ways to your best customers.
Final Thought
While finding intelligent life on other planets is, for now, limited to sci-fi films and books, finding audiences that share similar characteristics to your existing ones isn’t rocket science.